Rewards in the Core Chain Ecosystem
The Core Chain ecosystem is designed to incentivize participation and secure commitment from its community through a well-structured rewards system. This system underpins the Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, ensuring network security, stakeholder engagement, and alignment of interests among all participants. The rewards system is fundamental in encouraging the community to partake actively in mining, staking, and governance, thereby enhancing the overall health and growth of the ecosystem.
Types of Rewards
The reward structure on Core Chain is subject to adjustments based on periodic governance votes, allowing the community to respond to changes in the ecosystem, such as fluctuations in token value or shifts in the security landscape.
1. Mining Rewards
- Description: Mining rewards are provided to Bitcoin miners who contribute their hashing power to secure the Core Chain. This process extends the traditional mining efforts on the Bitcoin blockchain to include support for Core Chain, without requiring miners to divert resources from their Bitcoin mining activities.
- Mechanism: Miners include specific metadata in the Bitcoin blocks they mine, indicating their support for Core Chain. In return for their contribution, miners receive CORE tokens as supplemental rewards, on top of their regular Bitcoin mining rewards.
2. Staking Rewards
- Description: Staking rewards are distributed to BTC and CORE token holders who stake and delegate their tokens with Validators on the Core network. This staking not only helps secure the network through the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) component of the Satoshi Plus consensus but also enables token holders to participate in network governance.
- Mechanism: DPoS allows holders of both CORE tokens and Bitcoin to vote and participate in the election of the validator set by delegating their holdings to their preferred validators. For Core token staking, the minimum staking requirement is 1 CORE token, allowing any CORE holders to stake onto the Core network. On the bitcoin-staking side, the present configuration requires a minimum staking requirement of 0.01 BTC which is adjustable through a governance vote. Holders of both CORE token and BTC can delegate their respective tokens to validators of their choice through the official staking website. The rewards earned by stakers are proportional to the amount of BTC/CORE staked and the duration of the staking, incentivizing long-term holding and participation in the consensus process.
3. Validator Rewards
- Description: Validators earn rewards for their role in processing transactions, creating new blocks, and maintaining the blockchain's integrity. These rewards are critical for compensating Validators for their efforts and operational costs.
- Mechanism: Validators receive a combination of transaction fees and new CORE tokens minted through the blockchain's inflation policy. The amount of rewards a Validator receives is proportional to their stake and the delegated hash power from miners. There are two categories of validator rewards:
- Base rewards, i.e. newly minted CORE tokens;
- Fees collected from transactions in each block;
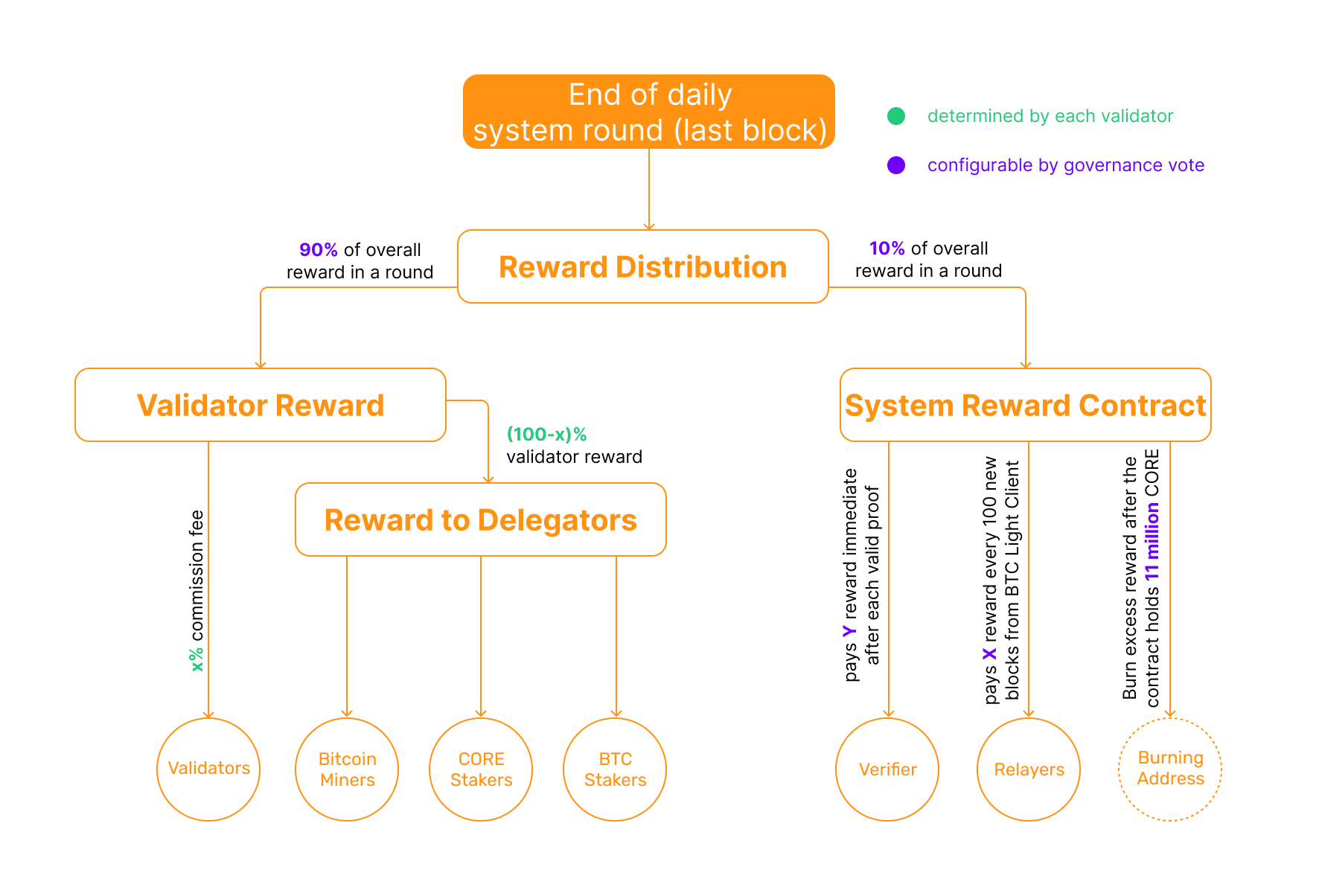
Base rewards are calculated and distributed when the last block of a round is mined. Currently, 90% of the rewards go to the validators and 10% of the rewards go to the System Reward Contract. Of the 90% paid to validators, some percentage is taken as a commission by the validator before they pay out their delegates. Each validator has an equal probability of producing blocks, so in the long run, all stable validators should get a similar portion of the reward.
Validators share rewards with the entities that delegated to them – including CORE stakers, bitcoin stakers, and PoW delegators – but they decide how much to give back by deciding how much they (the validators) choose to keep for themselves. Validators can take as much or as little of the reward as they want, though they’re incentivized to be generous in order to attract more stake and hash power.
After the validators take their fees, the protocol uses this function to determine how the remaining rewards are split between CORE stakers, BTC stakers, and hash power delegators. Reward distribution is calculated based on the following formula:
Where:
- is the rewards received by the validator because of the hash power delegated to it (DPoW)
- is the rewards received by the validator because of the CORE delegated to it (DPoS)
- is validator rewards attributed to BTC staking
- is the overall rewards attributed to all delegators
For completeness, here are three other ratios of interest:
Where:
- is the validator hash power rewards per unit;
- is the CORE token staking rewards per unit;
- is the BTC staking rewards per unit;
These reward-splitting functions are designed to create an active market for rewards while encouraging competition amongst the validator set for both delegated hash power and delegated stake. For their part, delegators will try to optimize their own rewards by choosing validators with lower amounts of delegated hash power and stake. To maximize their rewards, delegators will look both for validators that are generous in their payouts, but also don’t already have a substantial amount of delegated CORE tokens or delegated PoW. The less a given validator has staked, the greater a contribution from a delegator will be. If a delegator adds one CORE token to a validator that only has one token, they’re 50% of that validator’s total delegation. If they delegate to a validator with 99 CORE tokens, they’re only 1% of that validator’s total delegation. Since payouts are determined in part based on the percentage of total stake each delegator accounts for, they’ll be incentivized to try and find validators with small delegations.
4. Relayer and Verifier Rewards
In the Core Chain ecosystem, the base rewards are calculated and distributed when the last block of a round is mined, with 90% going to the validators and 10% to the System Rewards Contract. The System Reward Contract accumulates rewards to remunerate relayers and verifiers. As things stand, there is a cap of 10 million total CORE tokens in the System Reward Contract. Any rewards in excess of this amount are burned.
Relayers are responsible for communicating the Bitcoin block headers to the Core network. They earn a portion of the base system rewards and transaction fees for this cross-chain communications work. Relayer rewards are distributed in batches, every 100 Bitcoin blocks. Relayers claim their rewards periodically.
Verifiers in the Core Chain ecosytem are responsible for monitoring the behavior of validators and report them if they engage in double signing or other malicious activity. When successful, rewards are paid out immediately from the System Rewards Contract, in the same transaction.
5. Governance Participation Rewards:
- Description: Participants in the Core Chain governance process are incentivized through rewards that encourage active and thoughtful participation in decision-making processes.
- Mechanism: Rewards are distributed to users who vote on proposals and participate in other governance activities. These rewards aim to foster a proactive governance community and ensure that decisions reflect the broad consensus of the ecosystem’s stakeholders.
Reward Distribution Strategy
Core Chain follows the following distribution Principles:
- Fairness: The rewards system is designed to be fair, ensuring that contributions, whether in the form of staking, mining, or governance participation, are equitably recognized and rewarded.
- Transparency: All aspects of the reward distribution are transparent, allowing participants to understand how rewards are calculated and distributed.
- Security: The distribution mechanism is secured against manipulation and abuse, using cryptographic and smart contract-based safeguards to ensure the integrity of the reward process.
Conclusion
The rewards in the Core Chain ecosystem play a crucial role in maintaining the security, vitality, and decentralization of the network. By aligning the incentives of various participants through a comprehensive and adaptable rewards system, Core Chain ensures ongoing engagement and contributes to the sustained growth and stability of the platform. This structured approach to incentivization is foundational to the success of Core Chain as a leading platform in the Bitcoin DeFi landscape.