Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) in the Satoshi Plus Consensus Mechanism
Overview
Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) is a foundational component of the Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism on Core Chain. This innovative approach adapts the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) system used by Bitcoin, allowing for the integration of Bitcoin mining efforts into the security framework of a smart contract platform. DPoW maintains the robustness of Bitcoin’s security while enhancing its utility and economic incentives for miners. In the Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, validators are chosen on the basis of a hybrid score, and the hybrid score is calculated from both Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). In this section, we cover in depth the working and importance of DPoW in the functioning of the Satoshi Plus.
How DPoW Works in Satoshi Plus
On the Bitcoin network, Bitcoin miners generate hash power to secure the Bitcoin network, validate transactions, and earn BTC rewards. In order to even their rewards out over time, Bitcoin miners often contribute their hash power to mining pools, which use the aggregated hash power to increase the pool’s overall chances of mining a Bitcoin block and receiving BTC in return. DPoW integrates Bitcoin mining directly into the Core Chain's security protocol through a delegation system. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its operation:
-
Mining Integration: Bitcoin miners continue their standard mining activities but with the additional step of signaling their support for Core Chain. This is achieved by including a special transaction in the Bitcoin blocks they mine, which specifies the Core Validator they wish to support.
-
Metadata in Bitcoin Blocks: In the mined Bitcoin block, miners add metadata in the
op_returnfield. This metadata includes the address of the Core Validator and the address for receiving CORE token rewards, effectively delegating a portion of their hashing power to the Core Chain network. -
Validator Support: By including this information, miners delegate their computational power to Validators on the Core Chain. These Validators use the delegated power to participate in the Core Chain's version of block validation and creation.
-
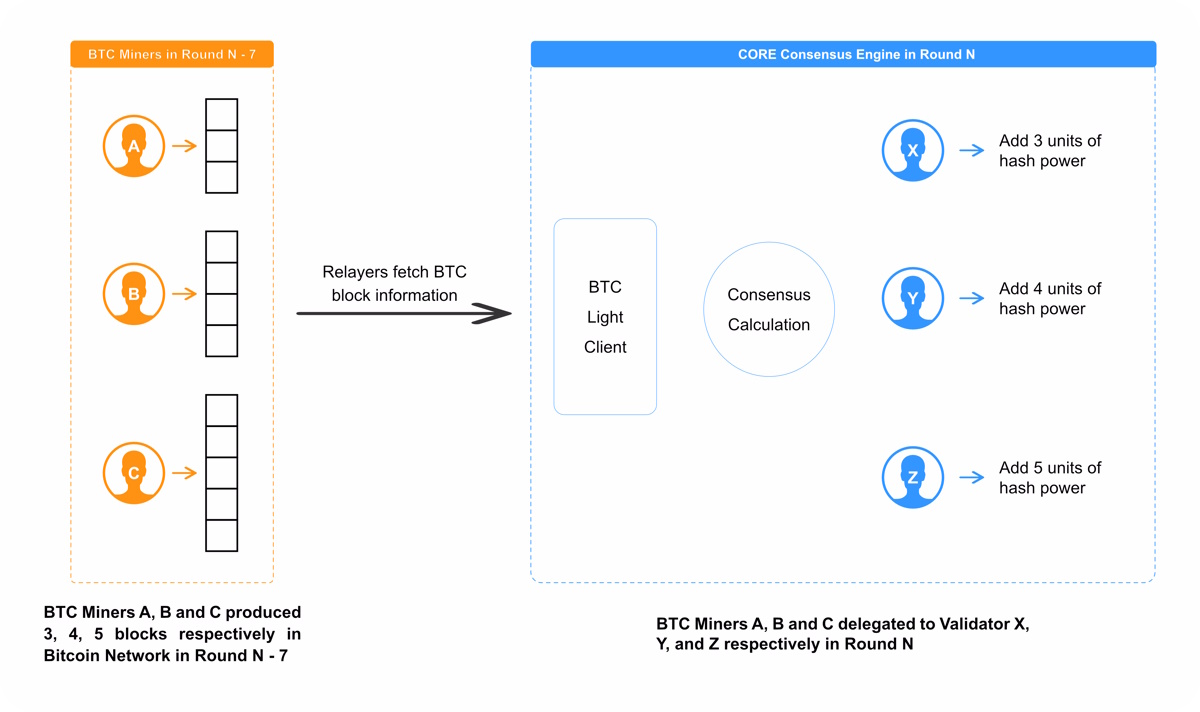
Relayers: The Bitcoin block headers make their way to Core Chain through Core Chain’s relayers. Each relayer runs an on-chain light client (or utilizes a similar, existing service) which syncs the blocks mined by the Bitcoin mining pool with the Core network. During a 1-day round, the Core network calculates the DPoW for each validator by counting the number of blocks the miners delegated to each validator one week prior. If the round occurs on a Thursday, for example, Core will tabulate the hash power delegated to each validator by counting blocks from last Thursday.
-
Reward Mechanism: In return for their contribution, miners receive additional rewards in the form of CORE tokens, on top of the usual Bitcoin mining rewards. This dual-reward system incentivizes miners to participate in the DPoW process without needing to divert resources away from Bitcoin mining.
The architecture for this cross-chain communication is illustrated in the diagram below.
Importance of DPoW in Satoshi Plus
-
Enhanced Security: DPoW leverages the immense hashing power of the Bitcoin network, which is the most secure blockchain network due to its extensive miner participation and proven cryptographic robustness. By integrating this power, Core Chain significantly enhances its own security.
-
Economic Incentives for Miners: The additional rewards in CORE tokens create a new revenue stream for Bitcoin miners, making mining operations more lucrative without increasing operational costs. This incentive is crucial in attracting more miners to participate in Core Chain's ecosystem.
-
Resource Efficiency: DPoW allows miners to maximize the utility of their existing computational resources. By supporting Core Chain while conducting their regular Bitcoin mining operations, miners can contribute to two networks simultaneously without additional energy expenditure.
-
Symbiotic Relationship: This mechanism creates a symbiotic relationship between Bitcoin and Core Chain. As Bitcoin miners contribute to the security of Core Chain, they enhance the overall value proposition of both networks. This interdependency aligns the interests of stakeholders across both platforms.
-
Sustainability: By reusing the hashing power already dedicated to Bitcoin mining, DPoW contributes to a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem. It reduces the need for additional energy consumption that would otherwise be required for securing a separate blockchain network.
Conclusion
DPoW is a critical innovation within the Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, marrying the proven security and decentralization benefits of Bitcoin’s PoW with the advanced capabilities of the Core Chain smart contract platform. This integration not only enhances the security and economic efficiency of both networks but also fosters greater miner participation and resource utilization, making it a pivotal component in the evolution of blockchain technology.